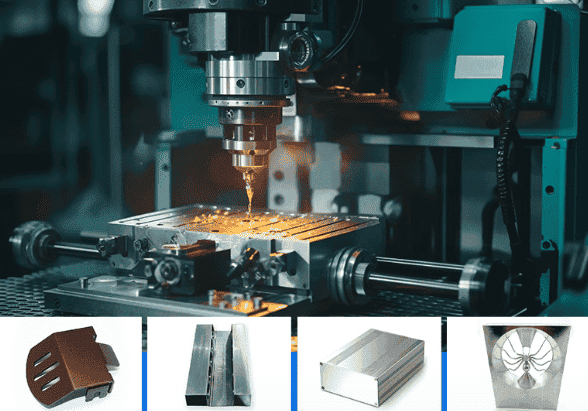
CNC Machining of Aluminum: Properties and Applications by TOP Prototype
Aluminum, with its unique combination of physical and mechanical properties, has become a preferred material in CNC machining across various industries. As a professional prototype and custom part manufacturer,TOP Prototype leverages the advantages of aluminum in CNC machining to deliver high-precision, high-quality components for clients worldwide. This article explores the key properties of aluminum that make it suitable for CNC machining and the diverse applications of aluminum CNC machined parts, highlighting TOP Prototype’s expertise in this field.
Aluminum is one of the commonly used materials in current machining. In fact, the CNC machining process for aluminum materials is second only to steel in terms of frequency of use.
In its high-purity form, the chemical element aluminum is soft, ductile, non-magnetic, and has a silvery-white appearance. However, this element is not used solely in its pure aluminum state. Aluminum is usually alloyed with various elements such as manganese, copper, and magnesium to form a variety of aluminum alloys with significantly improved properties. Common machining aluminum alloys and their designations under different standards can be found here.
Advantages of Using Aluminum for CNC Machined Parts

Although there are countless aluminum alloys with varying properties, all aluminum alloys share some basic characteristics:
Machinability
Aluminum can be quickly formed, manufactured, and processed through various treatment processes. It can be easily and rapidly cut by machine tools due to its soft texture, ease of cutting, low cost, and the lower force required compared to machining steel. These characteristics are great advantages for both machinists and customers ordering parts. Moreover, aluminum’s excellent machining performance means it is less prone to deformation during processing. Since it allows CNC machine tools to achieve higher tolerance, the precision is higher.
Specific Strength
The density of aluminum is approximately one-third that of steel, resulting in a relatively lighter weight. Despite its light weight, aluminum has very high strength. This combination of strength and weight is referred to as the specific strength of the material. Aluminum’s high specific strength makes it suitable for manufacturing many parts required by industries such as the automotive and aerospace industries.
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum is scratch-resistant and corrosion-resistant in conventional marine and atmospheric environments. This property can be further enhanced through anodization. It should be noted that the corrosion resistance of different grades of aluminum varies. Conventional general-purpose CNC machining grades actually have stronger resistance.
Low-Temperature Performance
Most materials lose some of their excellent properties below zero degrees Celsius. For example, carbon steel and rubber become brittle at low temperatures. In contrast, aluminum can maintain its softness, ductility, and strength at extremely low temperatures.
Electrical Conductivity
The electrical conductivity of pure aluminum at room temperature is approximately 37.7 million siemens per meter. Although aluminum alloys have lower electrical conductivity than pure aluminum, it is sufficient for applications in electronic components. On the other hand, if electrical conductivity is not the desired property of a machined part, aluminum will not be a suitable material for it.
Recyclability
Since the CNC machining process is a subtractive manufacturing process, it generates a large amount of chips, i.e., waste material. Aluminum has strong recyclability, and recycling requires relatively little energy, effort, and cost. This makes it highly favored by those looking to recover costs or reduce material waste. It also makes aluminum a more environmentally friendly processing material.
Anodization Potential
Anodization is a surface treatment process that improves the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of materials, and it is extremely easy to implement for aluminum. This process also makes it easier to color machined aluminum parts.
Popular Aluminum Alloys in CNC Machining
Based on our experience at Xometry, the following seven aluminum grades are commonly used in CNC machining:
(1)EN AW-2007 / 3.1645 / AlCuMgPb
– Other designations: 3.1645; EN 573-3; AlCu4PbMgMn
– This aluminum alloy is an aluminum-copper alloy, with copper as its main alloying element (accounting for 4%-5%). It is a short-chipping alloy that is durable, lightweight, and functional, with high mechanical properties similar to AW 2030.
– Suitable for tapping, heat treatment, and high-speed machining. All these characteristics of EN AW 2007 make it widely used in the production of mechanical parts, bolts, rivet nuts, screws, and deformed steel bars.
– Note: This grade of aluminum has poor weldability and corrosion resistance, so it is recommended to perform anodization after part processing for protection.
(2)EN AW-5083 / 3.3547 / Al-Mg4.5Mn
– Other designations: 3.3547; Alloy 5083; EN 573-3; UNS A95083; ASTM B209; AlMg4.5Mn0.7
– Alloy AW 5083 is known for its excellent performance in extreme environments. It contains magnesium and small amounts of chromium and manganese. This grade of aluminum exhibits very high corrosion resistance in chemical and marine environments.
– Among all non-heat-treatable aluminum alloys, it has higher strength, which can be maintained even after welding.
– Note: It is not suitable for use in environments with temperatures above 65 degrees Celsius, but performs excellently at low temperatures.
– Application scenarios: Low-temperature equipment, marine applications, pressure vessels, chemical applications, welded structures, and vehicle bodies, etc.
(3)EN AW 5754 / 3.3535 / Al-Mg3
– Other designations: 3.3535; Alloy 5754; EN 573-3; UNS A95754; ASTM B 209; Al-Mg3
– AW 5754 is an aluminum-magnesium alloy with a very high aluminum content, which can be rolled, forged, and extruded. It is also a non-heat-treatable aluminum alloy that can be strengthened through cold working but has relatively low ductility.
– In addition, this alloy has excellent corrosion resistance and high strength. Considering these properties, it is easy to understand why AW 5754 is one of the most popular aluminum materials for CNC machining.
– Application scenarios: Welded structures, floor coverings, fishing gear, vehicle bodies, food processing, and rivets, etc.
(4) EN AW-6060 / 3.3206 / Al-MgSi
– Other designations: 3.3206; ISO 6361; UNS A96060; ASTM B 221; AlMgSi0.5
– This is an aluminum alloy containing magnesium and silicon. It is heat-treatable, has medium strength, and good weldability and formability. It is also highly corrosion-resistant, and this property can be further improved through anodization.
– Application scenarios: Construction, food processing, medical equipment, and automotive engineering, etc.
(5)EN AW-7075 / 3.4365 / Al-Zn6MgCu
– Other designations: 3.4365; UNS A96082; H30; Al-Zn6MgCu
– In this grade of aluminum, zinc is the main alloying element. Although EN AW 7075 has average machinability, poor cold forming properties, and is not suitable for welding and brazing, it has high specific strength, excellent tolerance in atmospheric and marine environments, and higher strength than some steel alloys.
– Application scenarios: Hang gliders and bicycle frames, climbing equipment, weapons, and mold manufacturing, etc.
(6)EN AW-6061 / 3.3211 / Al-Mg1SiCu
– Other designations: 3.3211; UNS A96061; A6061; Al-Mg1SiCu
– The main alloying elements of this alloy are magnesium and silicon, with a small amount of copper. It is a high-strength alloy with a tensile strength of up to 180 megapascals, making it very suitable for high-load-bearing structures such as scaffolding, railway carriages, machinery, and aerospace parts.
(7)EN AW-6082 / 3.2315 / Al-Si1Mg
– Other designations: 3.2315; UNS A96082; A-SGM0.7; Al-Si1Mg
– This alloy is usually produced by rolling and extrusion, with medium strength, excellent weldability, and thermal conductivity. It has high resistance to stress corrosion cracking. The tensile strength ranges from 140 to 330 megapascals.
– Application scenarios: Widely used in marine construction and containers.
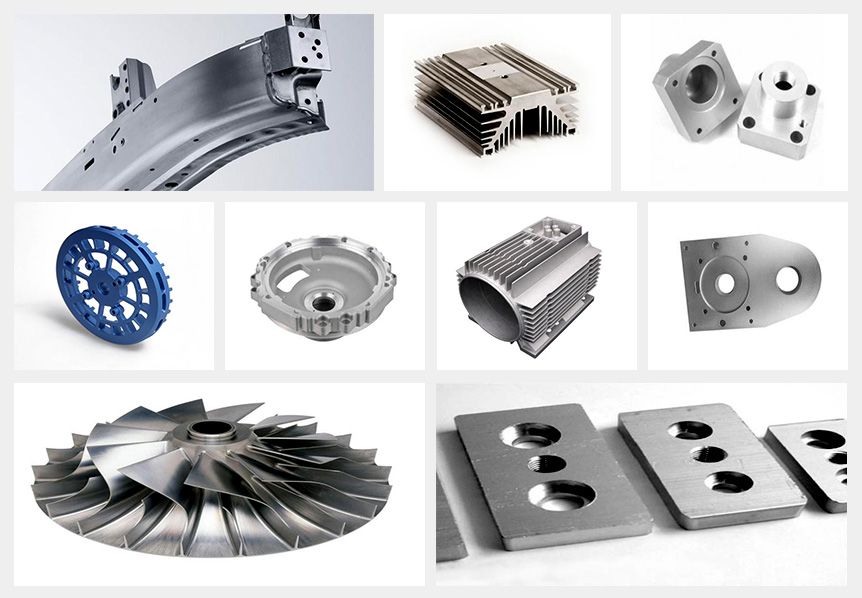
Industrial Applications of CNC Machined Aluminum Parts
As mentioned above, aluminum alloys possess many desirable properties. Therefore, CNC machined aluminum parts are indispensable in many industries, as follows:
– Aerospace: Due to the high specific strength of aluminum alloys, many aircraft components are made of machined aluminum.
– Automotive Manufacturing: Similar to the aerospace industry, many components in the automotive industry, such as drive shafts and other parts, are also made of aluminum.
– Electrical: CNC machined aluminum parts are often used as electronic components in household appliances due to their high electrical conductivity.
– Food/Pharmaceutical: Aluminum parts do not react with most organic substances, so they play an important role in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
– Sports: Aluminum is often used to make sports equipment such as baseball bats and sports whistles.
– Low-Temperature Applications: Aluminum can maintain its mechanical properties below zero degrees Celsius, making aluminum parts highly popular in low-temperature applications.
In summary, the exceptional properties of aluminum make it a versatile choice for CNC machining, catering to the diverse needs of multiple key industries. TOP Prototype, with its profound expertise in CNC machining technology and in-depth understanding of aluminum materials, is well-equipped to provide customized, high-precision aluminum machined parts. Whether for aerospace, automotive, electrical, or other specialized applications, TOP Prototype is committed to delivering reliable, high-quality solutions that meet and exceed client expectations, driving innovation and efficiency across various industrial sectors.